链表 链表相关的核心点
NULL 异常处理
dummy node(哑巴节点)
快慢指针
插入一个节点到排序链表
从一个链表中移除一个节点
翻转链表
合并两个链表
找到链表的中间节点
哑巴节点 哑节点(dummy node)是初始值为NULL的节点,创建在使用到链表的函数中,可以起到避免处理头节点为空的边界问题的作用,减少代码执行异常的可能性。也就是说,哑节点的使用可以对代码起到简化作用 (省略 当函数的入口参数为空时的判断 )。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 struct ListNode { int val; struct ListNode *next; }; ListNode *addNode ( ListNode *node, int num) { struct ListNode *new = (struct ListNode*) malloc (sizeof (struct ListNode) * num); node->next = new ; return new ; } ListNode *addNode ( ListNode *node, int num) { struct ListNode *new = (struct ListNode*) malloc ( sizeof (struct ListNode) * num ); if ( null == node ){ return new ; } node->next = new ; return new ; } struct ListNode *dummyNode= (struct ListNode*) malloc (sizeof (struct ListNode));dummyNode->val = NULL ; dummyNode->next = NULL ; ListNode *addNode ( ListNode *dummyNode, int num) struct ListNode *new = (struct ListNode*) malloc ( sizeof (struct ListNode) * num ); dummyNode->next = new ; return new ; }
快慢指针 快慢指针就是定义两根指针,移动的速度一快一慢,以此来制造出自己想要的差值。这个差值可以让我们找到链表上相应的节点。 比如,我们把一个链表看成一个跑道,假设a的速度是b的两倍,那么当a跑完全程后,b刚好跑一半,以此来达到找到中间节点的目的。
常见题型 删除排序链表中的重复元素
给定一个排序链表,删除所有重复的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class Solution {public : ListNode* deleteDuplicates (ListNode* head) { if (head == NULL ) { return head; } if (head->next){ head->next = deleteDuplicates (head->next); if (head->val == head->next->val) { head = head->next; } } return head; } }; class Solution {public : ListNode* deleteDuplicates (ListNode* head) { ListNode* current = head; while (current) { while (current->next && current->val == current->next->val) { current->next = current->next->next; } current = current->next; } return head; } };
删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
给定一个排序链表,删除所有含有重复数字的节点,只保留原始链表中 没有重复出现的数字。
思路:链表头结点可能被删除,所以用dummy node辅助删除
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 class Solution {public : ListNode* deleteDuplicates (ListNode* head) { if (head == NULL ) return head; if (head->next && head->val == head->next->val) { while (head->next && head->val == head->next->val) { head = head->next; } return deleteDuplicates (head->next); } else { head->next = deleteDuplicates (head->next); } return head; } }; class Solution {public : ListNode* deleteDuplicates (ListNode* head) { if (head == NULL ) { return head; } struct ListNode *dummyNode= (struct ListNode*) malloc (sizeof (struct ListNode)); dummyNode->next = head; head = dummyNode; int temp; while (head->next && head->next->next) { if (head->next->val == head->next->next->val) { temp = head->next->val; while (head->next && head->next->val == temp) { head->next = head->next->next; } } else { head = head->next; } } return dummyNode->next; } };
注意点
反转链表
反转一个单链表。
思路:用一个prev节点保存向前指针,next保存向后的临时指针
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution {public : ListNode* reverseList (ListNode* head) { if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL ) { return head; } ListNode* ret = reverseList (head->next); head->next->next = head; head->next = NULL ; return ret; } }; class Solution {public : ListNode* reverseList (ListNode* head) { ListNode *next = NULL ; ListNode *prev = NULL ; while (head) { next = head->next; head->next = prev; prev = head; head = next; } return prev; } };
反转链表 II
反转从位置 m 到 n 的链表。请使用一趟扫描完成反转。
思路:先遍历到 m 处,翻转,再拼接后续,注意指针处理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 class Solution {public : ListNode* successor = NULL ; ListNode* reverseN (ListNode* head, int n) { if (n == 1 ) { successor = head->next; return head; } ListNode* last = reverseN (head->next, n - 1 ); head->next->next = head; head->next = successor; return last; } ListNode* reverseBetween (ListNode* head, int m, int n) { if (m == 1 ) { return reverseN (head, n); } head->next = reverseBetween (head->next, m - 1 , n - 1 ); return head; } }; class Solution { public : ListNode* reverseBetween (ListNode* head, int m, int n) { if (head == NULL ) { return head; } ListNode* dummyNode = (struct ListNode*)malloc (sizeof (struct ListNode)); dummyNode->next = head; head = dummyNode; ListNode* pre = NULL ; int i = 0 ; while (i < m) { pre = head; head = head->next; i++; } int j = i; ListNode* next = NULL ; ListNode* mid = head; while (head != NULL && j <= n) { ListNode* temp = head->next; head->next = next; next = head; head = temp; j++; } pre->next = next; mid->next = head; return dummyNode->next; } };
合并两个有序链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的升序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
思路:通过 dummy node 链表,连接各个元素
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 class Solution {public : ListNode* mergeTwoLists (ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) { if (l1 == nullptr ) { return l2; } else if (l2 == nullptr ) { return l1; } else if (l1->val < l2->val) { l1->next = mergeTwoLists (l1->next, l2); return l1; } else { l2->next = mergeTwoLists (l1, l2->next); return l2; } } }; class Solution { public : ListNode* mergeTwoLists (ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) { if (l1 == NULL ) { return l2; } else if (l2 == NULL ) { return l1; } ListNode* dummyNode = (struct ListNode*)malloc (sizeof (struct ListNode)); ListNode* head = dummyNode; while (l1 != NULL && l2 != NULL ) { if (l1->val < l2->val) { head->next = l1; l1 = l1->next; } else { head->next = l2; l2 = l2->next; } head = head->next; } while (l1 != NULL ) { head->next = l1; head = head->next; l1 = l1->next; } while (l2 != NULL ) { head->next = l2; head = head->next; l2 = l2->next; } return dummyNode->next; } };
分隔链表
给定一个链表和一个特定值 x,对链表进行分隔,使得所有小于 x 的节点都在大于或等于 x 的节点之前。
思路:将大于 x 的节点,放到另外一个链表,最后连接这两个链表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { public : ListNode* partition (ListNode* head, int x) { if (head == NULL ) { return head; } ListNode* headDummy = (struct ListNode*)malloc (sizeof (struct ListNode)); headDummy->next = head; head = headDummy; ListNode* tailDummy = (struct ListNode*)malloc (sizeof (struct ListNode)); ListNode* tail = tailDummy; while (head->next) { if (head->next->val < x) { head = head->next; } else { ListNode* temp = head->next; head->next = head->next->next; tail->next = temp; tail = tail->next; } } tail->next = NULL ; head->next = tailDummy->next; return headDummy->next; } };
哑巴节点使用场景
当头节点不确定的时候,使用哑巴节点
排序链表
在 O (n log n ) 时间复杂度和常数级空间复杂度下,对链表进行排序。
思路:归并排序,找中点和合并操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 class Solution { public : ListNode *sortList (ListNode *head) { return (head == NULL ) ? NULL : mergeSort (head); } private : ListNode *findMid (ListNode *head) { ListNode *slow = head; ListNode *fast = head; ListNode *previous = NULL ; while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL ) { previous = slow; slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; } previous->next = NULL ; return slow; } ListNode *mergeTwoLists (ListNode *l1, ListNode *l2) { if (l1 == NULL ) return l2; if (l2 == NULL ) return l1; if (l1->val < l2->val) { l1->next = mergeTwoLists (l1->next, l2); return l1; } else { l2->next = mergeTwoLists (l1, l2->next); return l2; } } ListNode *mergeSort (ListNode *head) { if (head->next == NULL ) return head; ListNode *mid = findMid (head); ListNode *l1 = mergeSort (head); ListNode *l2 = mergeSort (mid); return mergeTwoLists (l1, l2); } };
注意点
快慢指针 判断 fast 及 fast->next 是否为 NULL 值
递归 mergeSort 需要断开中间节点
递归返回条件为 head 为 NULL或者 head->next 为 NULL
重排链表
给定一个单链表 L :L →L →…→L__n →L 将其重新排列后变为: L →L__n →L →L__n →L →L__n →…
思路:1.快慢指针找到中点 2.拆成两个链表 3.遍历两个链表,后面的塞到前面的“缝隙里”
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 class Solution { public : void reorderList (ListNode *head) if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL ) return ; ListNode *slow = head; ListNode *fast = head; while (fast->next && fast->next->next) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; } ListNode *needReverser = slow->next; slow->next = NULL ; needReverser = reverseList (needReverser); ListNode *cur = head; while (cur && needReverser) { ListNode *curSecond = needReverser; needReverser = needReverser->next; ListNode *nextCur = cur->next; curSecond->next = cur->next; cur->next = curSecond; cur = nextCur; } } ListNode *reverseList (ListNode *head) { if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL ) { return head; } ListNode *ret = reverseList (head->next); head->next->next = head; head->next = NULL ; return ret; } ListNode *reverse (ListNode *head) { ListNode *next = NULL ; ListNode *prev = NULL ; while (head) { next = head->next; head->next = prev; prev = head; head = next; } return prev; } };
环形链表
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
思路:快慢指针,快慢指针相同则有环(因为fast快,slow慢,所以如果有环fast最后一定会追上slow),
证明:如果有环每走一步快慢指针距离会减 1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { public : bool hasCycle (ListNode *head) if (!head || !head->next) { return false ; } ListNode *slow = head; ListNode *fast = head; while (fast->next && fast->next->next) { if (!slow->next) { return false ; } slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; if (fast == slow) { return true ; } } return false ; } }; fast = head->next; slow = head;
环形链表 II
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
思路:快慢指针,快慢相遇之后,慢指针回到头,快慢指针步调一致一起移动,相遇点即为入环点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution {public : ListNode *detectCycle (ListNode *head) { if (!head || !head->next) { return NULL ; } bool hasCycle = false ; ListNode *slow = head; ListNode *fast = head; while (fast->next && fast->next->next) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; if (fast == slow) { hasCycle = true ; break ; } } if (hasCycle) { slow = head; while (slow != fast) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next; } return slow; } return NULL ; } };
坑点
指针比较时直接比较对象,不要用值比较,链表中有可能存在重复值情况
第一次相交后,快指针需要从下一个节点开始和头指针一起匀速移动
回文链表
请判断一个链表是否为回文链表。
取中间分开链表,反转后面的链表,如果和前面的重合则为回文链表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 class Solution {public : ListNode *reverse (ListNode *head) { ListNode *next = NULL ; ListNode *prev = NULL ; while (head) { next = head->next; head->next = prev; prev = head; head = next; } return prev; } bool isPalindrome (ListNode* head) if (head == NULL ) { return true ; } ListNode *left = head; ListNode *right = head; while (right->next && right->next->next) { left = left->next; right = right->next->next; } ListNode *middle = reverse (left); left->next = NULL ; while (middle && head) { if (head->val != middle->val) { return false ; } head = head->next; middle = middle->next; } return true ; } };
复制带随机指针的链表
给定一个链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。 要求返回这个链表的深拷贝。
思路:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 class Solution {public : Node* copyRandomList (Node* head) { if (!head) { return head; } Node* cur = head; while (cur) { Node* clone = new Node (cur->val, NULL , NULL ); clone->next = cur->next; Node* temp = cur->next; cur->next = clone; cur = temp; } cur = head; while (cur) { if (cur->random != NULL ) { cur->next->random = cur->random->next; } cur = cur->next->next; } cur = head; Node* new_head = head->next; Node* new_tail = new_head; while (cur) { cur->next = cur->next->next; if (new_tail -> next != NULL ) { new_tail->next = new_tail->next->next; } cur = cur->next; new_tail = new_tail->next; } return new_head; } };
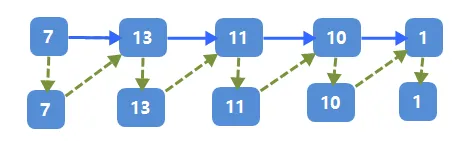
是不是看不懂复制节点那一步,图解在这。
总结 链表必须要掌握的一些点,通过下面练习题,基本大部分的链表类的题目都是手到擒来~
null/nil 异常处理
dummy node 哑巴节点
快慢指针
插入一个节点到排序链表
从一个链表中移除一个节点
翻转链表
合并两个链表
找到链表的中间节点